In this post, we will see a detailed explanation of String Handling in Java with an example.
Introduction
String in Java is an important concept while writing java programs and learning Java. You must know what is String in Java, How is it useful.
String, which is widely used in Java Programming, is a sequence of characters. The Java Platform provides the String class to create and manipulate the Strings.
For Example "welcome" is a string containing a sequence of characters which is 'w','e','l','c','o','m','e'. And String are represents as double-quotes.
For example,
String name="John";
String Objects are Immutable:
String objects are fixed. Every time we create a string, a new object is created. Working on an immutable string is efficient than that of a mutable String.
Mutable classes: StringBuffer and StringBuilder
String in Java is a final and immutable class means we can not change or alter the object. It cannot be inherited once it is created.
Creating Strings:
There are two ways to create String,
1. String Object:
Create String Object Using new keyword
As with any other object, you can create String Objects by using the new keyword and a constructor.
For Example,
String strObj = new String("Hello World");
2. String Literals:
Create a String object using double quotes
String strName1="Beautiful";
String strName2="Beautiful";
Whenever it encounters a string literal in your code, the compiler creates a String object with its value in the constant pool.
Whenever there are two string literals with the same value assigned to it. The compiler will assign that two two string objects to the same string value.
for instance in the above string literal example,
If the (strName1)object already exist in the memory it does not create a new Object rather it assigns the same old object to the new instance, that means even though we have two string instances above(strName1 and strName2) compiler only created on string object (having the value “Beautiful”) and assigned the same to both the instances. For example, there are 20 string instances that have the same value, it means that in-memory there is only one object having the value and all the 20 string instances would be pointing to the same object.
else If you want to have two different objects with the same string..for that we need to use the new keyword to create two different objects as explained above.
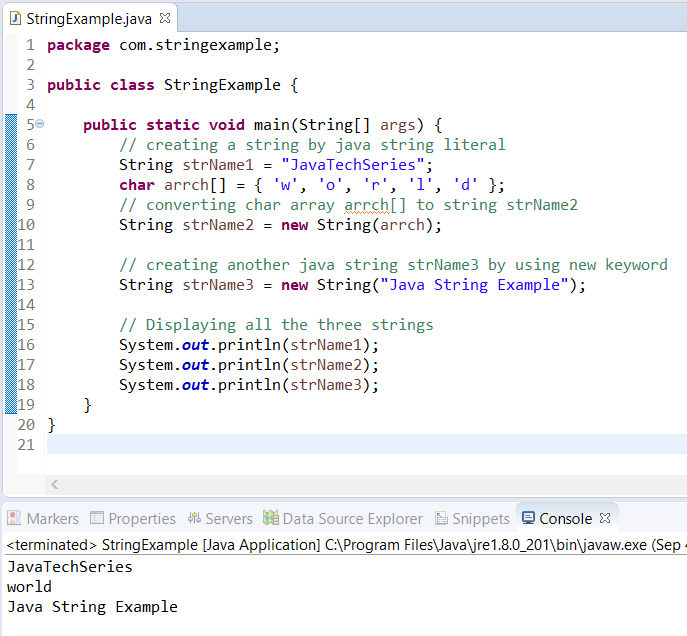
Java String Example:
Eclipse IDE Code:
Java String Methods:
Here is the list of the explained methods available in the Java String class.
|
Methods |
DESCRIPTION |
|
String concat(String str) |
It
concatenates that is Joins the two string together, join the str at the end. |
|
int length() |
It returns the size of the specified String |
|
boolean equals(Object obj) |
It compares
the value of the two string, if matches it returns true else false. |
|
boolean contains(CharSequence cs) |
It checks whether the string contains the
specified sequence of char values. If yes then it returns true else false. It
throws NullPointerException of ‘s’ is null. |
|
char charAt(int index) |
It returns the character at the specified
index. Specified index value should be between 0 to length() -1 both
inclusive. It throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if index<0||>= length of
String. |
|
int indexOf(int ch) |
Returns the index of first occurrence of the
specified character ch in the string. |
|
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) |
Same as indexOf method however it starts
searching in the string from the specified fromIndex. |
|
int lastIndexOf(int ch) |
It returns the last occurrence of the character ch in the string. |
|
int lastIndex(int ch, int fromIndex) |
Same as lastIndexOf(int ch) method, it
starts search from fromIndex. |
|
int indexOf(String str) |
This method returns the index of first occurrence of specified substring str. |
|
int lastIndex(String str) |
Returns the index of last occurrence of
string str. |
|
boolean startWith(String prefix) |
It tests whether the string is having
specified prefix, if yes then it returns true else false. |
|
boolean endsWith(String suffix) |
Checks whether the string ends with the
specified suffix. |
|
String substring(int beginIndex) |
It returns the substring of the string. The
substring starts with the character at the specified index. |
|
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) |
Returns the substring. The substring starts
with character at beginIndex and ends with the character at endIndex. |
|
byte[] getBytes() |
This method is similar to the above method
it just uses the default charset encoding for converting the string into
sequence of bytes. |
|
byte[] getBytes(String charSetName) |
It converts the String into sequence of
bytes using the specified charset encoding and returns the array of resulted
bytes. |
|
static String valueOf() |
This method returns a string representation
of passed arguments such as int, long, float, double, char and char array |
|
int hashCode() |
It returns the hash code of the string. |
|
String replace(char newchatr, char oldchar) |
It returns the new updated string after changing all the occurrences of oldChar with the newChar. |
|
String replaceFirst(String regex, String
replacement) |
It replaces the first occurrence of substring
that fits the given regular expression “regex” with the specified replacement
string. |
|
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) |
It replaces all the occurrences of
substrings that fits the regular expression regex with the replacement string. |
|
String[] split(String regex, init limit) |
It splits the string and returns the array
of substrings that matches the given regular expression. limit is a result
threshold here. |
|
String[] split(String regex) |
Same as split(String regex, int limit) method however it does not have any threshold limit. |
|
String toLowerCase(Locale locale) |
It converts the string to lower case string
using the rules defined by given locale. |
|
public static String format() |
This method returns a formatted java String |
|
String trim() |
Returns the substring after omitting leading
and trailing white spaces from the original string. |
|
String toUpperCase(Locale locale) |
Converts the string to upper case string
using the rules defined by specified locale. |
|
String toUpperCase() |
Equivalent to
toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault()). |
|
public String intern() |
This method searches the specified string in
the memory pool and if it is found then it returns the reference of it, else
it allocates the memory space to the specified string and assign the
reference to it. |
|
public Boolean isEmpty() |
This method returns true if the given string
has 0 length. If the length of the specified Java String is non-zero then it
returns false. |
|
public static String join() |
This method joins the given strings using
the specified delimiter and returns the concatenated Java String |
|
boolean matches(String index) |
It checks whether the String is
matching with the specified regular expression regex. |
|
int codePointAt(int index) |
It is similar to the charAt method however
it returns the Unicode code point value of specified index rather than the
character itself. |
|
boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) |
It compares the string to the specified
string buffer. |
|
boolean regionMatches(int sroffset, String dest,
int destoffset, int len) |
It compares the substring of input to the
substring of specified string |
|
boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int
sroffset, String dest, int destoffset, int len |
Another variation of regionMatches method
with the extra boolean argument to specify whether the comparison is case
sensitive or case insensitive. |
|
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) |
It works same as equals method but it
doesn’t consider the case while comparing strings. It does a case insensitive
comparison. |
|
int compareTo(String str) |
This method compares the two strings based
on the Unicode value of each character in the strings. |
|
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) |
Same as CompareTo method however it ignores
the case during comparison. |
|
boolean startsWith(String prefix, int offset) |
It checks whether the substring (starting
from the specified offset index) is having the specified prefix or not. |
|
static String copyValueOf(char[] data) |
It returns a string that contains the
characters of the specified character array. |
|
static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset,
int count) |
Same as above method with two extra
arguments – initial offset of subarray and length of subarray. |
|
void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dest,
int destBegin) |
It copies the characters of src array
to the dest array. Only the specified range is being
copied(srcBegin to srcEnd) to the dest subarray(starting fromdestBegin). |
|
char[] toCharArray() |
Converts the string to a character array. |
That's all about a detailed explanation of String Handling in Java, We discussed all string methods and the introduction of String in java in an easily understandable concept. I hope you enjoyed this post!!
Recommended String Programs:
Check entered String is Magic or not


ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon